基础
数据类型
数组
索引数组
索引数组是一种特殊的数组
例如a = np.array([0, 11, 22, 33, 44, 55])indices = np.array([1, 3, 5])a 的元素selected = a[indices]selected 就是一个新的数组a 的第 13 和第 5 个元素[11, 33, 55]
列表
元组
字典
集合
字符串
控制流
函数
异常处理
函数式编程
PPL 中的高阶函数
高阶函数 map()
高阶函数 filter()
高阶函数 reduce()
匿名函数 / lambda 表达式
面向对象编程
语法糖
装饰器
生成器
迭代器
列表推导式
实战
使用 Python 计算常见四搭型的牌效率
麻将中常见复合型的进张情况
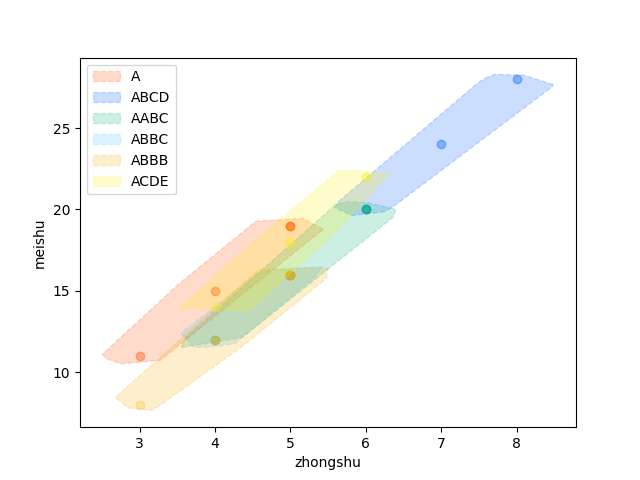
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Polygon
import numpy as np
import random
from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
# 回溯法计算是否是有效的听牌形式或胡牌形式(不含国士)
def is_jinzhang_OK(arr):
arr = arr.copy()
arr.sort()
if not arr:
return True
# 刻子
if arr.count(arr[0]) >= 3:
new_arr = arr.copy()
new_arr.remove(arr[0])
new_arr.remove(arr[0])
new_arr.remove(arr[0])
if is_jinzhang_OK(new_arr):
return True
# 顺子
if arr[0] + 1 in arr and arr[0] + 2 in arr:
new_arr = arr.copy()
new_arr.remove(arr[0])
new_arr.remove(arr[0] + 1)
new_arr.remove(arr[0] + 2)
if is_jinzhang_OK(new_arr):
return True
# 对子, 两面, 坎张的情况的处理是类似的, 此处略去
return False
# 列表中对应位置处的元素代表对应数牌是否是有效进张
def jinzhang(arr):
return [0] + [is_jinzhang_OK(arr + [i]) for i in range(1, 10)]
# 进张种数
def jinzhang_zhongshu(arr):
return jinzhang(arr).count(True)
# 计算除了这个搭子外, 所有数牌的残余数量
def shengyu_meishu(arr):
return [0] + [(4 - arr.count(i)) for i in range(1, 10)]
# 进张枚数
def jinzhang_meishu(arr):
remaining = shengyu_meishu(arr)
jinzhang_result = jinzhang(arr)
return sum([(remaining[i] * jinzhang_result[i]) for i in range(1, 10)])
# 生成所有的单张数牌
def generate_all_A():
return [[i] for i in range(1, 10)]
# 生成所有的 ABCD 型搭子
def generate_all_ABCD():
arrays = []
for i in range(6):
arrays.append([1 + i, 2 + i, 3 + i, 4 + i])
return arrays
# ...
# 单张数牌 A 的情况
arrays0 = generate_all_A()
x0 = [jinzhang_zhongshu(arr) for arr in arrays0]
y0 = [jinzhang_meishu(arr) for arr in arrays0]
points0 = [(x + random.uniform(0, 0.5), y + random.uniform(0, 0.5)) for x, y in zip(x0, y0)]
points0 += [(x - random.uniform(0, 0.5), y + random.uniform(0, 0.5)) for x, y in zip(x0, y0)]
points0 += [(x - random.uniform(0, 0.5), y - random.uniform(0, 0.5)) for x, y in zip(x0, y0)]
points0 += [(x + random.uniform(0, 0.5), y - random.uniform(0, 0.5)) for x, y in zip(x0, y0)]
# 生成凸包并绘制
hull0 = ConvexHull(points0)
points0_np = np.array(points0)
plt.scatter(x0, y0, color='#FF4B00', alpha=0.2)
poly0 = Polygon(points0_np[hull0.vertices], fill=True, color='#FF4B00', alpha=0.2, linestyle='dashed', label='A')
plt.gca().add_patch(poly0)
plt.xlabel('zhongshu')
plt.ylabel('meishu')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
使用 PIL 库将多张图片合并成一个网格
在文件夹中.xxx 的图片.xxx 拼接为一张图output-{timestamp}.xxx 到当前工作目录下
生成的图片的长宽将取决于每行每列被拼接图片数量
import os
import time
import argparse
from PIL import Image, ImageOps
# 创建命令行参数解析器, 并解析命令行参数
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Combine images into a grid.')
parser.add_argument('image_folder', help='The folder containing the images.')
parser.add_argument('image_format', help='The format of the images (e.g., .png, .jpg).')
parser.add_argument('num_rows', type=int, help='The number of rows in the grid.')
parser.add_argument('num_cols', type=int, help='The number of columns in the grid.')
parser.add_argument('--rotate', type=int, choices=[0, 90, 180, 270], help='The angle to rotate each image.')
parser.add_argument('--log', action='store_true', help='Log the process.')
args = parser.parse_args()
timestamp = int(time.time())
# 获取图片文件夹中的所有图片文件, 按文件名排序, 只保留前 num_rows * num_cols 张图片
image_files = sorted([os.path.join(args.image_folder, file) for file in os.listdir(args.image_folder) if file.endswith(args.image_format)])
image_files = image_files[:args.num_rows * args.num_cols]
images = [Image.open(image_file) for image_file in image_files]
# 如果指定了旋转角度, 就旋转每一张图片, 并获取旋转后的宽度和高度
if args.rotate:
images = [image.rotate(args.rotate, expand = True) for image in images]
image_widths_and_heights = [(image.getbbox()[2] - image.getbbox()[0], image.getbbox()[3] - image.getbbox()[1]) for image in images]
image_width = max(width for (width, height) in image_widths_and_heights)
image_height = max(height for (width, height) in image_widths_and_heights)
else:
image_width = max(image.size[0] for image in images)
image_height = max(image.size[1] for image in images)
total_width = image_width * args.num_cols
total_height = image_height * args.num_rows
if args.log:
print(f'Max image width: {image_width}, max image height: {image_height}\n')
print(f'Total width: {total_width}, total height: {total_height}\n')
# 遍历图片列表, 将每一张图片粘贴到新的图片上的正确位置
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (total_width, total_height), (255, 255, 255))
for index, image in enumerate(images):
row = index // args.num_cols
col = index % args.num_cols
# 创建一个新的空白图片 background , 大小为最大宽度和高度, 将图片居中粘贴到背景图片上
background = Image.new('RGB', (image_width, image_height))
offset = ((image_width - image.size[0]) // 2, (image_height - image.size[1]) // 2)
background.paste(image, offset)
# 将 background 粘贴到新的图片上的正确位置
new_image.paste(background, (col * image_width, row * image_height))
if args.log:
print(f'Pasted image {index} at offset: {offset}, at position: {(col * image_width, row * image_height)}\n')
new_image.save(f'output-{timestamp}{args.image_format}')
比较坑的地方是使用 image.rotate() 方法并不会自动调整图像的宽度和高度image.getbbox() 方法来获取图像的边界框x, y 坐标image.rotate() 方法时需要指定 expand = True
使用 PIL 库将多张图片合并成 pdf 文件并使用图像的平均哈希值去重
import os
import time
import argparse
from PIL import Image
import imagehash
# 创建命令行参数解析器, 并解析命令行参数
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Output images as a PDF file, each image on a separate page, removing duplicates.')
parser.add_argument('image_folder', help='The folder containing the images.')
parser.add_argument('image_format', help='The format of the images (e.g., .png, .jpg).')
parser.add_argument('--rotate', type=int, choices=[0, 90, 180, 270], help='The angle to rotate each image.')
parser.add_argument('--log', action='store_true', help='Log the process.')
args = parser.parse_args()
timestamp = int(time.time())
# 获取图片文件夹中的所有图片文件, 按文件名排序
image_files = sorted([os.path.join(args.image_folder, file) for file in os.listdir(args.image_folder) if file.endswith(args.image_format)])
unique_images = []
hashes = []
for image_file in image_files:
current_image = Image.open(image_file)
current_hash = imagehash.average_hash(current_image)
# 检查当前图片与已有图片的相似度
if not any(current_hash - h < 5 for h in hashes):
unique_images.append(current_image)
hashes.append(current_hash)
elif args.log:
print(f'Skipped duplicate image: {image_file}')
# 如果指定了旋转角度, 就旋转每一张图片
if args.rotate:
unique_images = [image.rotate(args.rotate, expand=True) for image in unique_images]
# 使用第一张图片作为封面, 其余图片追加到 PDF 中
if unique_images:
last_folder_name = os.path.basename(os.path.normpath(args.image_folder))
pdf_path = f'{last_folder_name}-{timestamp}.pdf'
unique_images[0].save(pdf_path, "PDF", resolution=100.0, save_all=True, append_images=unique_images[1:])
if args.log:
print(f'Saved {len(unique_images)} images to {pdf_path}')
为当前文件夹内每一个 .md 文件添加更新时间
import os
import datetime
directory = '.'
for file in os.listdir(directory):
if file.endswith('.md'):
full_path = os.path.join(directory, file)
mod_time = os.path.getmtime(full_path)
readable_time = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(mod_time).strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
update_string = f"updated: {readable_time}\n"
with open(full_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
if len(lines) >= 3:
lines.insert(3, update_string)
else:
lines.append(update_string)
with open(full_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.writelines(lines)